Pregnancy weeks 1 to 4 has been created to guide you through the changes happening during pregnancy (conception). During pregnancy weeks 1 to 4 hormonal changes that you may be unaware of are happening at rapid rates, please read further to find out about the development of your egg to a foetus with this guide of pregnancy weeks 1 to 4. At week 1 of pregnancy through to week 4 pregnancy and the first official ultrasound scan of your baby.
Pregnancy Week 1

Pregnancy Week 1 is officially the week of your last menstural period although it is very difficult to predict exactly when the first week of pregnancy actually is because of not knowing exactly when the sperm fertilized your egg (ovum).
However, even in the first week of pregnancy the conception is already preparing itself to take place now that the body is assuming to conceive in the next few days. To begin this preparation of the body the levels of Oestrogen rise as it has to be ready for the presumed conception. As the oestrogen levels raise the eggs (ovums) in the ovaries start to mature and ripen ready for the pregnancy that is expected to happen.
The cervix lubricates itself with a special mucus like fluid that acts as a carrier for the sperm helping it to travel more easily to the waiting eggs (ovums). This mucus protects the sperm and keeps them in the cervix for almost five days giving them ample chanes to fertilize the waiting egg (ovum).
Sexual intercourse should be perfectly timed when you are trying to conceive, although this can be a difficult technique to master, sexual intercourse can be increased to enhance your chances of pregnancy and the most fertile time for a women to conceive is said to be 3 – 5 days before ovulation.
Pregnancy Week 2
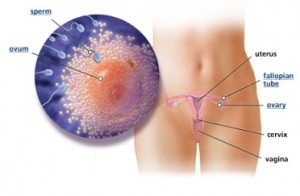
During week 2 of pregnancy the body releases more oestrogen which makes the uterus form a lining of tissue in preparation to support the new life of the foetus.
This lining of tissue is preparing to support the fertilized egg once it reaches the uterus. The levels of progesterone also rise within the body to help the uterus prepare to support the fertilized egg.
The body is now almost ready to conceive, small fluid filled sacs from the ovaries are released into the fallopian tubes where they sit and wait for the sperm to complete the process of pregnancy.
Foetal development at 14 Days Pregnant
The embryo is a ball of cells that are constantly preparing for the changes yet to come with the development of the pregnancy. The embryo at one side starts dividing cells into one large bunch that will after about 8 weeks of pregnancy become the foetus. The embryo cells at the other side make a fluid filled sac which after 8 weeks of pregnancy will become the amniotic fluid that the fetus will float around and survive in.
The amniotic fluid filled sac is a thin membranous bag made up of amnion and chorion that will be protection for the fetus cushioning the fetus from pressure from the mothers internal organs, but also allowing the foetus movement.
Pregnancy Week 3

Pregnancy Week 3 can be a confusing time for you with changes happening in your body at the time that your new menstrual cycle would have been due. Week 3 is usually worked out from the start of your last menstrual cycle yet your baby may only have been conceived during the previous week, also this being the week before the expected menstrual cycle would have been due.
Foetal Development at 21 Days Pregnant
The mass of cells that will form the baby called the blastocyst begins a process of implantation. This implantation process is where the blastocyst embeds itself securely into the womb lining. The implantation process is done efficiently without the mother feeling her baby or even knowing that she is carrying a baby as very little discomfort is felt upto completion that can take upto 7 days and normally ends a few days before the expected menstrual cycle would have been starting.
The embedded blastocyst releases a hormone called human gonadotrophin hormone into the body stopping the coming menstrual cycle from happening, at the same time the implantation process has been completed and the mother and her soon to become baby are attached in the womb, the blood of the mother is shared with the blastocyst providing it with fulfilling nourishment, replacing the sugary sweet source that was obtained from the fallopian tubes and uterus.
Rarely some women do feel a slight discomfort during the implantation process of the blastocyst and thick, heavy bleeding can occur which can be confused with the next menstrual period as it happens at the time when the period was expected. The blastocyst goes through many changes once implanted , the cells within the blastocyst itself start moving to one side and multiply at an alarming rate. The cells are transforming all the time and are starting to form three layers called the Endoderm, the Mesoderm and the Ectoderm.
The Endoderm is the production of the babies vital internal organs that form the liver, lungs, bowel and bladder. The Mesoderm is the production of the babies bone structure, heart and muscles and sex organs. The Ectoderm is the production of the babies eyes, ears, skin, brain, spinal cord and lastly the hair.
During this productive period the other side of the blastocyst is also transforming into two layers one which is producing the life support system for the baby in the form of afterbirth which is called the placenta. The second layer is forming the amniotic sac which gradually fills up with amniotic fluid ready to cushion and protect the forming foetus. Many women do not even realise at this stage that they are pregnant and put the minor sensations felt down to a menstrual period.
Pregnancy Week 4

Pregnancy week 4 is when most women discover that they are pregnant and start to accept their unborn foetus. The foetus at 4 weeks of pregnancy is still just a ball of cells dividing within the uterus to become the embryo. The placenta and umbilical cord are in early stages of development and are already starting to feed the embryo with nutrition and oxygen.
You are now 4 weeks pregnant and at this time you should be due to have your menstrual period which is late! This is where most women discover their pregnancy.
Foetal Development at 28 Days Pregnant
The balstocyst is from now on referred to as the embryo and measures less than 2mm. On the 18th day post conception the baby within you has already began to form the spinal cord and brain which is also referred to as the Neural Tube.
The ectoderm (which is the top layer of the divided cells of the blastocyst) starts to form the rear of the embryo. This is done when the two flat sheet of cells crease in the centre and begin to wrap around themselves to make a tube which will become the spinal cord. The spinal cord stretches and at one end starts to expand into what will become the brain of the embryo although these are very early stages and will take at least the rest of week 4 of pregnancy to complete the process and finish at the end of the week where the two sheets of cells eventually meet and bond together to become the Neural Tube.
The endoderm (which is the bottom layer of the divided cells of the blastocyst) start to protrude at the frontal chest area of the embryo and form a sac containing yolk for vital nutrition and fluids that will feed the embryo initially until the umbilical cord is formed. The body of the embryo forms a type of stalk that extends from the waistline of the embryo.
This stalk will eventually form into the umbilical cord within the body of the embryo and will start to accept nutrition when the placenta is developed and fully functional, meanwhile until this process is complete the sac containing the yolk will feed the embryo enough to allow the liver, lungs, bowel and bladder of the embryo to form. A blood supply for the embryo will also form through the nutrition provided from the sac containing yolk.
Ultrasound at 4 Weeks Pregnant

Ultrasound Scans at 4 weeks pregnant can be tricky to find, but detection of the pregnancy at week 4 is possible. The visible images are of a tiny sac and can often be missed due to the minute size of the sac. Some inexperienced ultrasonographers have trouble locating the pregnancy, but as you can see this scan shows the developing foetus quite clearly.